Is That Video Real? A Guide to Spotting AI-Generated Content
Imagine scrolling through a social media feed and encountering a video that looks incredibly real, yet a subtle sense of unease lingers.
In today's evolving digital world, this feeling is becoming increasingly common as artificial intelligence (AI) achieves remarkable feats in creating videos that are almost indistinguishable from authentic footage. Tools like Google's new Veo 3 are pushing the boundaries of what's possible, generating "shockingly realistic videos that are quickly becoming ommonplace on social media.
This isn't merely about fun filters or creative experiments; it's about discerning what's authentic from what's fabricated, especially as AI-generated content can be used for "misinformation" or "nefarious purposes".
The increasing sophistication of AI-generated content, particularly video, is fundamentally reshaping how individuals perceive and trust digital information. What was once a clear distinction between authentic and fabricated media is now blurring, creating a landscape where visual evidence can no longer be blindly accepted.
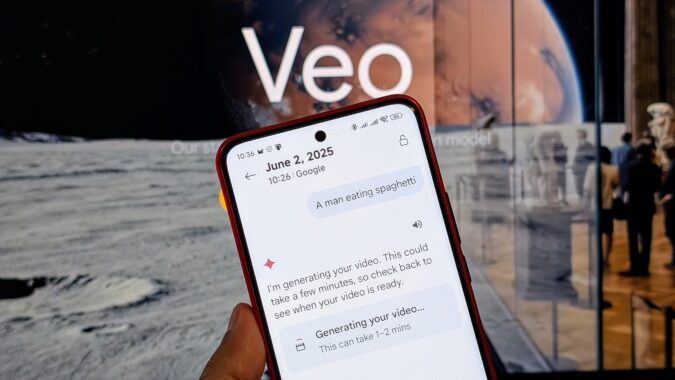
Google's Veo 3, unveiled at Google I/O 2025, represents a leap forward in AI video generation. Designed to transform text or image prompts into high-definition videos, it initially creates clips up to 8 seconds in length.
What makes Veo 3 particularly noteworthy is its ability to produce native audio output, including synchronized dialogue, ambient sounds, and background music, making clips feel remarkably lifelike. This capability sets it apart from earlier models like Sora or Runway, giving it a significant edge. Veo 3 also boasts features such as maintaining consistent characters in different video clips and offering new ways to fine-tune camera angles, framing, and movements.
Veo 3's ability to produce remarkably lifelike videos, complete with synchronized dialogue and rich soundscapes, establishes a new benchmark for AI-generated content. This level of realism makes it a powerful creative tool, but it also amplifies its potential for deception. Consequently, the subtle imperfections that still exist within Veo 3's output become even more crucial for viewers to identify, as the overall convincing nature of the video might otherwise mask these tell-tale signs.
However, it is important to remember that even advanced AI has its limits. While shockingly realistic, some Veo 3 videos still exhibit a glossy aesthetic and jerky camera movements.
Early tests also show that the model can break when prompts venture into unfamiliar territory or become too subtle. Even with advanced AI like Veo 3, the digital world often struggles to perfectly mimic the intricate details of human appearance and the laws of physics.
Here’s what a discerning eye can reveal:
A. Faces and Bodies
1. Unnatural Blinking
– Humans blink frequently, typically around 15-20 times per minute. AI-generated characters might blink too rarely, too often, or at strangely robotic, inconsistent intervals. Paying close attention to the eyes—if they seem unnaturally static or the blinking pattern feels "off"—can be an indicator.
2. Waxy or Inconsistent Skin:
– Real skin possesses pores, subtle blemishes, and varied textures. AI-generated skin can often appear unnaturally smooth, waxy, or exhibit inconsistent details, lacking the natural imperfections that make a face truly human.
3. Odd or Distorted Features
– Look for abnormalities that AI frequently struggles with. This includes hands with extra fingers or too many teeth , odd finger placement , blurry teeth outlines, or teeth that do not seem to change naturally as the mouth moves. Facial features might also appear asymmetrical.
4. Stiff or Jerky Movements
– While AI can simulate broader human movements, it often misses the subtle fluidity and naturalness of human motion. Watch for stiffness, awkward or jerky movements , or facial expressions that seem delayed, misaligned with the emotions, or simply "off". Veo 3 itself has been noted for jerky camera movements.
5. Lip-Sync Issues
– One of the classic giveaways. If the mouth movements do not perfectly match the words being spoken, or if they appear slightly out of sync, it is a strong indicator of AI manipulation.
6. Pupil Dilation Problems
– Natural pupils react to changes in light. In AI videos, they might remain unnaturally static, or their size might be inconsistent with the lighting or even mismatched between the two eyes.
7. Character Consistency (Veo 3 Specific)
– While Veo 3 aims for consistent characters in different video clips , this feature is described as a bit fragile. It may be observed that while a character's facial structure remains similar, their clothes changed across shots, or other visual details are not perfectly maintained.
Beyond specific visual cues, many AI-generated videos, despite their high quality, can evoke a subtle sense of unease. This phenomenon, often described as the uncanny valley, occurs when something appears almost human but not quite, leading to a feeling of discomfort.
When observing a video, if a subject's movements or expressions feel subtly "off", a stiffness in their smile, an unnatural fluidity in their walk, it is often a reliable indicator that the content may be AI-generated. Trusting this intuitive feeling can be a powerful first line of defense, even before analyzing specific technical flaws.
B. Lighting and Environment
1. Inconsistent Shadows and Reflections
– AI often struggles with the complex physics of light. Look for shadows that do not align logically with visible light sources, or reflections (in eyes, glasses, water, or shiny surfaces) that appear unnatural or misplaced. A face might appear glowing unnaturally in dim environments.
2. Warped or Strange Backgrounds
– The background might look distorted, hazy, or contain "unusual details". Objects might "appear and disappear" unexpectedly, "morph unexpectedly," or take "unusual forms".
3. Unnatural Textures or Halo Effects
– Sometimes, AI video enhancement or upscaling can introduce subtle visual artifacts like "unnatural textures or halo effects around edges".
Despite their advanced capabilities, AI models still face challenges in perfectly replicating the intricate laws of physics and the complexities of human biology. This fundamental limitation often manifests in visual discrepancies. For instance, the way light interacts with objects and casts shadows, or how human eyes naturally blink and pupils dilate in response to light, involves subtle physical interactions that AI models, while making highly sophisticated estimations, do not yet fully simulate. These "educated guesses" can lead to inconsistencies that, once recognized, become clear indicators of AI generation.
Google is actively working to combat misinformation by embedding an imperceptible watermark called SynthID into content generated by its AI tools, including Veo 3. This watermark is designed to provide "provenance tools" and remain detectable even if the content is shared or altered. Google has launched the SynthID Detector,na verification portal where individuals can upload images, audio, or video files. The portal then scans for the SynthID watermark and highlights the specific portions of the content where it is detected.
Google's SynthID represents a step forward in promoting transparency by embedding invisible digital watermarks into AI-generated content, including videos created by Veo 3. This innovative technology aims to provide a reliable way to trace the origin of digital media.
However, it is important to understand that even advanced watermarking systems, while highly effective, are not entirely infallible. Creators with malicious intent can, through extreme modifications, potentially bypass these embedded markers. Therefore, while the presence of a watermark offers strong evidence of AI generation, its absence does not definitively guarantee a video's authenticity, highlighting the ongoing challenge in the digital content landscape.
It is important to note that currently, the SynthID Detector is being rolled out to "early testers" such as journalists, media professionals, and researchers. While not yet widely available to the general public, Google expects broader access "in the coming months".
Checking the Source: Who Posted This?
Always consider the source of the video. Examine the account that posted it:
a. Account History: Is it a new account? Does it have an "erratic posting pattern" or primarily share viral content without original uploads?
b. Follower Patterns: Does the account have "bot-like followers" (e.g., many followers but zero posts from them)?.
Content Consistency: Does the account consistently upload videos from a specific location or with a consistent style, or does it seem to "scrape" videos from various news organizations or other accounts?
If a video makes a significant claim, especially concerning real-world events or individuals, always "verify the information through credible sources". Check established news outlets, official websites, or reputable fact-checking organizations. Be cautious if a video "lacks context, information about its source," or an easy way to verify its authenticity.
While new technologies like SynthID offer valuable assistance, some of the most effective strategies for discerning authentic content from AI-generated fabrications are rooted in fundamental media literacy practices that have been relevant for decades. Scrutinizing the source of a video, examining the posting account's history and patterns, and cross-referencing claims with established, credible news outlets or official sources are timeless verification techniques. These practices remain indispensable, demonstrating that human critical thinking and investigative skills are, and will continue to be, the most robust defense against misinformation, regardless of how the content was produced.